So we know plants use photosynthesis to produce glucose (if not check out my article on Photosynthesis), but how does this actually give our bodies energy? Both plants and animals use a process called cellular respiration to convert glucose into usable energy for life processes.
This is the equation for (aerobic) cellular respiration: C6H12O6 (glucose) + O2 –> CO2 + H20
Now what do you notice? Cellular respiration is the exact opposite of photosynthesis, but the processes themselves are vastly different. It’s important to know that while photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts, respiration occurs in the mitochondria, which is a shared organelle between both plants and animals.
Glycolysis
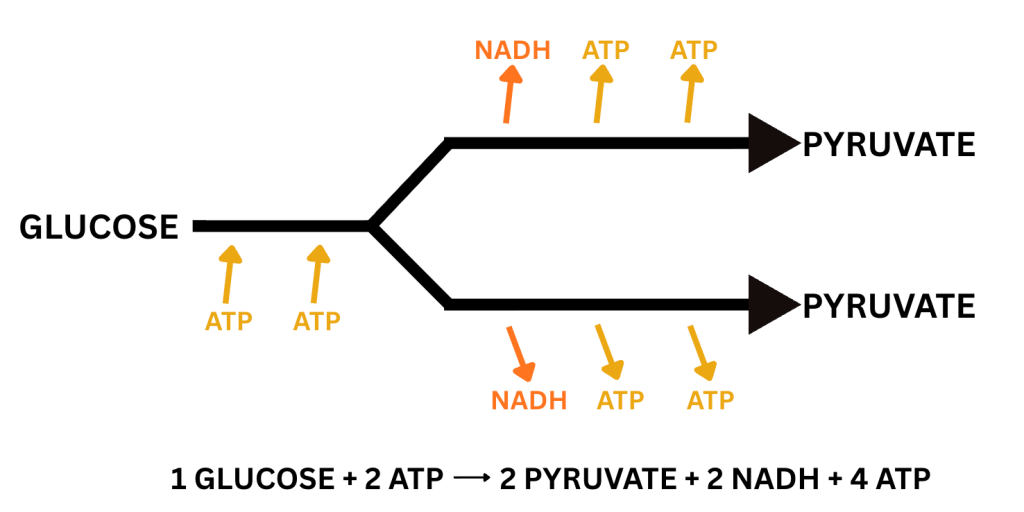
Glucose enters the cell, either through photosynthesis or consumption. It is then broken down into two 3-carbon molecules called pyruvate with the help of pre-existing ATP (energy). This produces a small amount of ATP and high-energy electron carriers called NADH.
Krebs Cycle
After being produced during glycolysis, the two pyruvate molecules move to the mitochondria. There, they enter the Krebs Cycle, where they undergo a series of enzymatic reactions which ultimately produce more ATP and high-energy electron carriers (NADH + FADH2). NADH and FADH2 release their hydrogen ions and electrons to be carried on the electron transport chain and CO2 diffuses out.
Electron Transport Chain
Electrons are shuttled back and forth across the inner mitochondrial membrane, releasing energy to pump protons (H+). At the end of the chain, oxygen accepts the electrons as well as hydrogen protons to form water (H20) in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Finally, the enzyme ATP synthase adds phosphate to ADP (used energy) using energy from the protons to produce ATP. This ultimately produces 32 molecules of ATP (per glucose molecule).
FEATURED ARTICLE
Why Is Taylor Swift So Popular?
Whether you love or hate her, Taylor Swift is one of the biggest names of our generation. But what makes her so popular? Why her? Early Career It’s important to know that Taylor started out as a country star; moving to Nashville at 13 to pursue her passion for music. Given her standout songwriting abilities…




Leave a comment